What is FDM 3D printing?

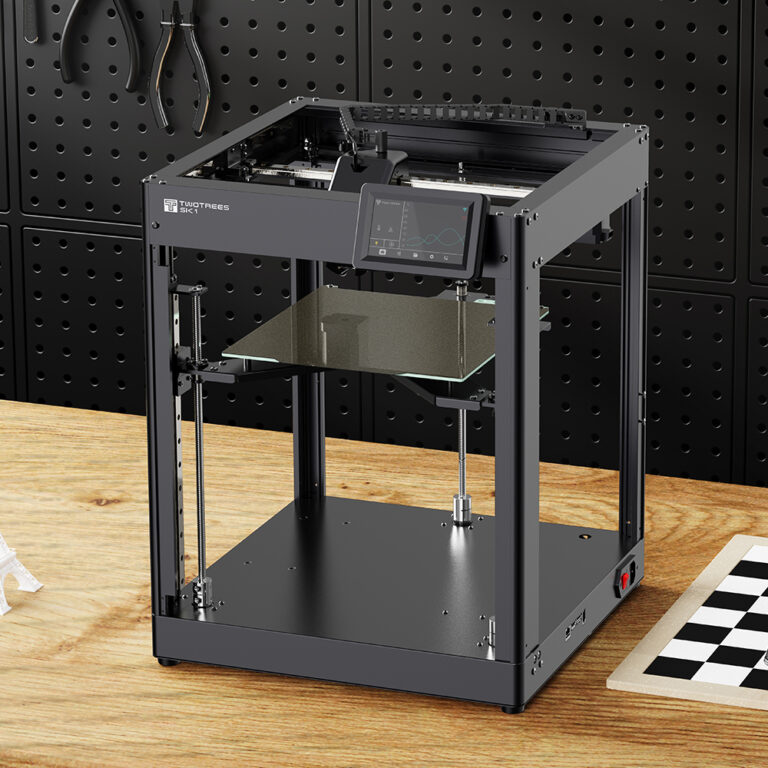
FDM 3d Printer Anatomy & Diagram

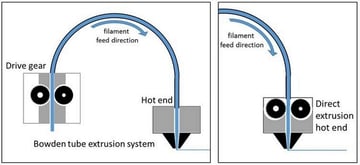
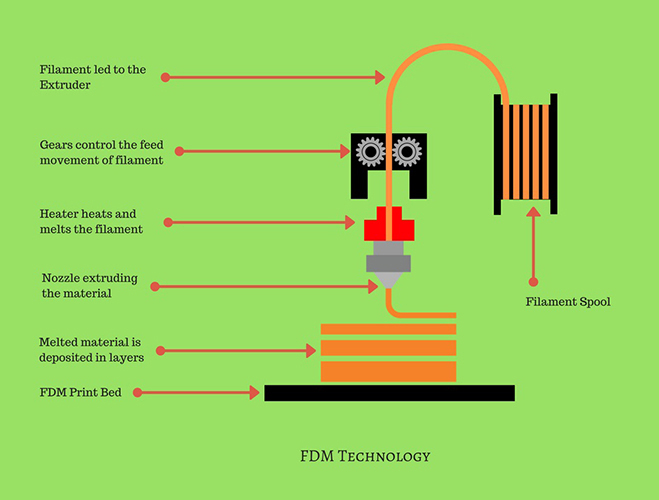
How Does A FDM 3D Printer Work Explained with Gif
Step One: 3D Modeling
After setting up your 3D printers, the real challenge for beginners shows up: what to print with. To get printing started, the first thing to do would get a 3D printer file/mode (STL is the most popular file format). For users without knowledge to build 3D models by themselves, the easy solution would be sourcing free STL 3D printing files from websites like Thingiverse or Cult.

Step Two: 3D Model Slicing
As mentioned in FDM 3D printing definition, the printers need a computer file to tell it how to move its printing nozzle and printing hotbed. The slicing file basically does this job as it tells printers two-dimensional images of each layer, filaments thickness applied to each layer and the gap distance between each layer. If you already get a 3D modeling file at hand, there are a few popular slicing software to help you slice the 3D model file (STL file) into sliced one(usually in GCode format).

Step Three: FDM 3D Filaments Extrusion
Before starting printing, users need to turn on 3D printers for pre-heating to make the printing nozzle and hotbed temperature reach configured temperature. When the temperature reaches the pre-set temperatures, filaments would be pushed from the filaments holder forwarder to the printing nozzle for melting and printing.
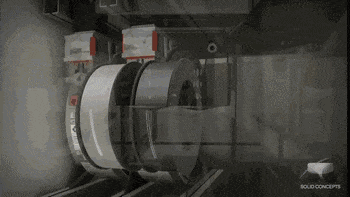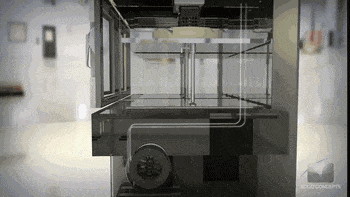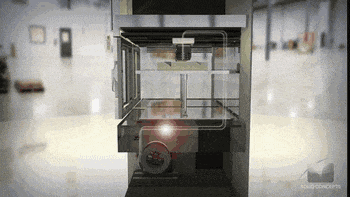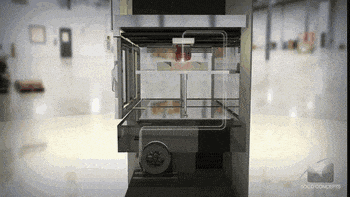
Step Four: Adding Melted Filaments Layer by Layer

After melted filaments get to the printing nozzle, the nozzle and printing hotbed would move in a direction that is configured in the slicing file. For a standard cartesian FDM 3D printer, the printing nozzle would move left and right along the X-axis, the printing hotbed platform would move forwarder and backward in a Y-axis, the X-axis would move up and down along the mainframe. There are also CoreXY FDM 3D printers like our SP series with auto-leveling hotbeds to increase printing stability and accuracy.
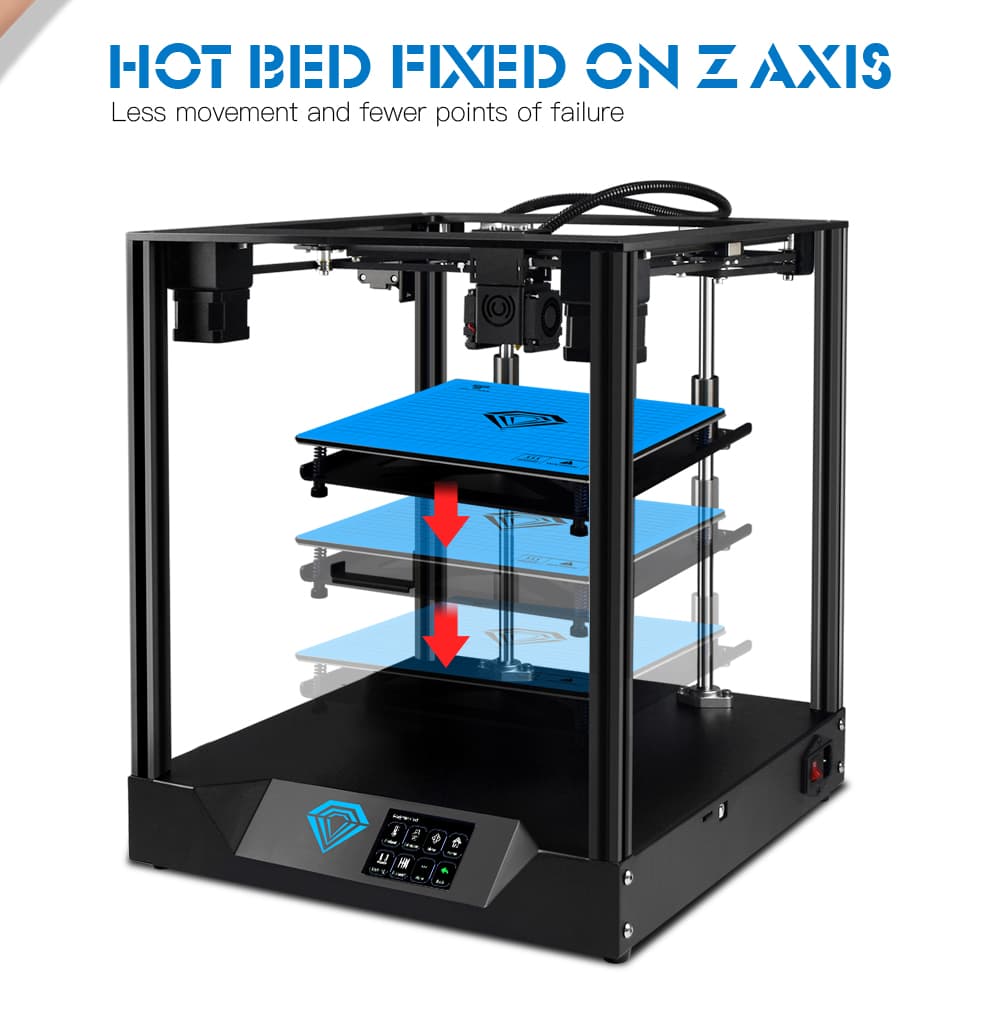

Step Five: Removing Supports
Supporting bridges is another important factor for getting great FDM 3D prints. As filaments are added layer by layer, if the upper layer in the design file does not have enough contacting area, the upper layer would tend to slide down before fully solidating due to gravity. Thus supporting bridges are introduced to offer extra supporting force to avoid deformation. After printing is finished, the supporting structure needs to be removed to get the designed models.

Step Six: Post-processing
Though supporting bridges be removed, there would still be some remains on the surface which would affect final results. Thus, users still need to smooth up the surface to get a decent and smooth surface for coloring.

FDM 3D Printer Materials
Conclusion
FDM 3D printer is the most popular 3D printer in the market and also a great choice for 3D printing beginners. Understanding how it works would help users quickly target possible reasons if the printer does not work properly. Getting decent prints requires some technics and tricks and if you are interested in this topic, please signup for our newsletter and stay updated with us.